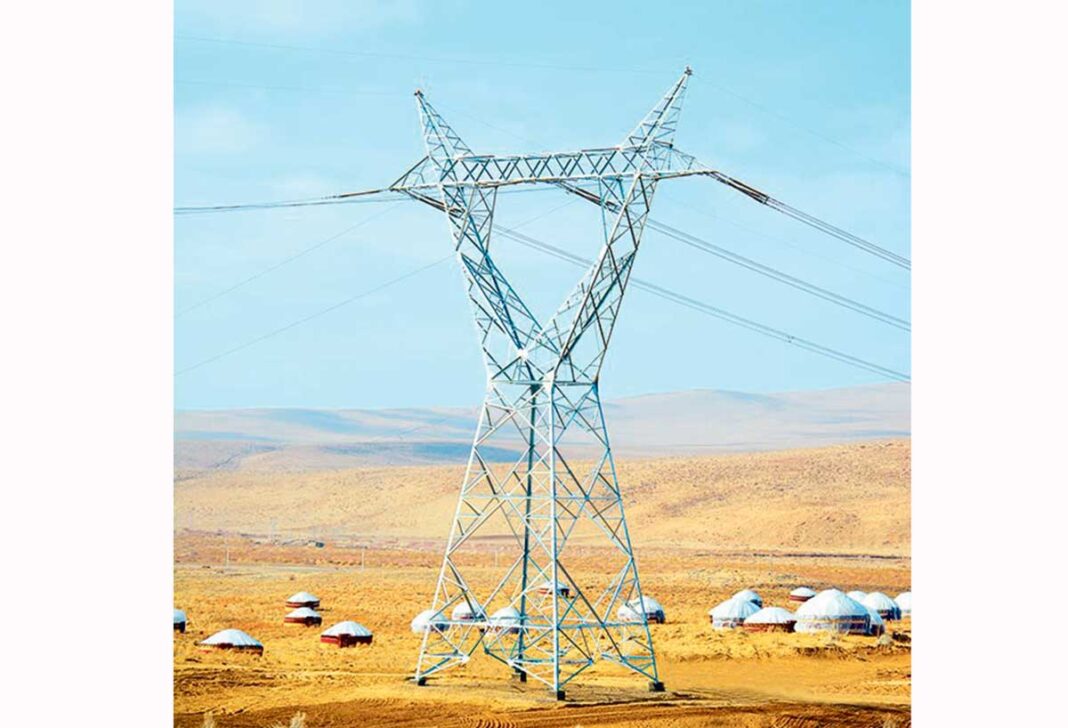
Electric power remains a key sector of the Turkmenistan economy. The country is currently focusing on balancing capacity growth with reducing environmental impact. Energy-saving technologies are being implemented to save fuel and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Smart grids have become the foundation of this modernization, according to the country’s Information Center.
Automated energy distribution allows the system to quickly respond to load changes, prevent accidents, and redistribute resources during peak hours, protecting the infrastructure from wear and tear.
The legislative framework for these changes is enshrined in the laws “On Energy Saving and Energy Efficiency” and “On Renewable Energy Sources.” The state is introducing preferential lending, tax incentives, and customs exemptions for the import of modern equipment.
Special attention is being paid to energy audits of buildings and resource consumption standards. This strengthens energy independence and increases the responsibility of businesses and citizens for the environment.
One effective solution is the combined-cycle power generation cycle. It uses the heat from exhaust gases for additional generation, increasing the efficiency of power plants. The Mary hydroelectric power plant, with a capacity of 1574 MW, has demonstrated success, and a similar facility is being built in the Balkan welayat. The transition to a combined cycle reduces natural gas consumption while maintaining generation capacity.
At the same time, green technologies are being developed within the framework of the National Strategy to 2030. The first multifunctional solar-wind power plant with a capacity of 10 MW is being built in the Gyzylarbat etrap, which will provide remote regions with clean and affordable energy.
Combined with the modernization of transmission networks and digital control, these measures allow Turkmenistan to fully meet domestic demand and increase electricity exports.